Have you ever asked about water chemistry “what’s the difference between pH and alkalinity for betta fish? Many of us in aquatics confuse total alkalinity and pH. It’s understandable, given how blurred the line is between words like “alkaline” and “alkalinity.” Indeed, alkalinity and pH in water chemistry are closely related, but they are not the same. This article will distinguish between them.

What is pH?
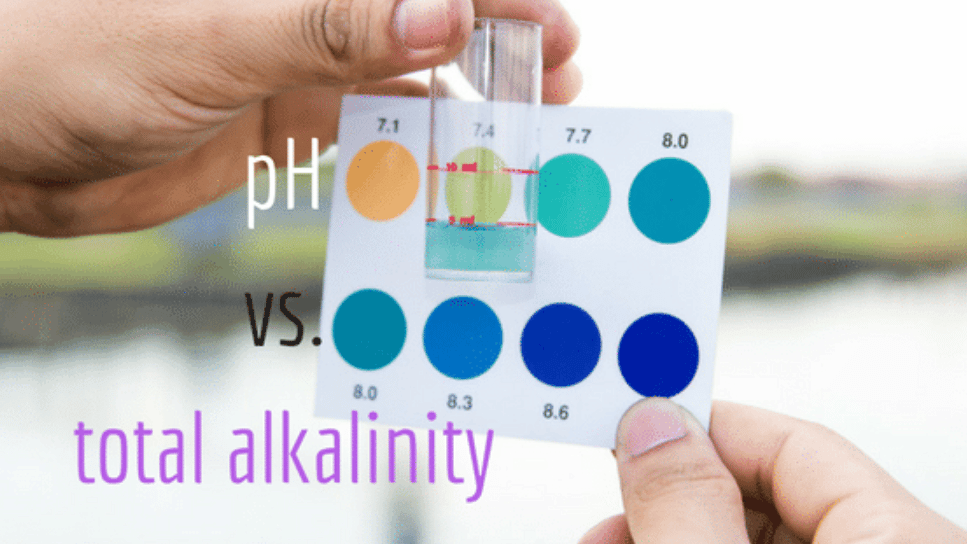
We measure how acidic or basic (also called alkaline) substances are by using the pH scale. The pH scale goes from 1 to 14, and is relative to pure water, which has a perfectly neutral pH of 7. pH stands for “power of Hydrogen;” the measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The pH is a negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration:
pH = -log(H+)
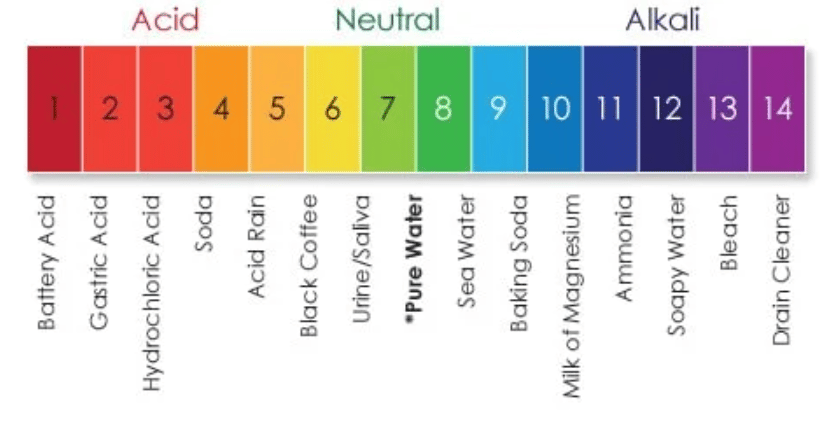
When the concentration of hydrogen ions goes up, the pH goes down. And vice versa. The scale is logarithmic, which means each whole number on the 1-14 pH scale is 10 times more or less than the numbers around it. For example, something with a pH of 6 would be 10 times more acidic than pure water. Something with a pH of 5 is 10 times more acidic than 6, which means it’s 100 times more acidic than pure water (10×10=100).
To put the pH scale in perspective, let’s do some quick math. Trichlor, a popular type of stabilized chlorine used primarily in outdoor pools, has a pH of about 3. For this math, let’s just round it to exactly 3.0. How acidic is 3.0pH Trichlor compared to 7.0pH pure water? Let’s figure it out.
(7.0pH – 3.0pH) = 4.0
Logarithmic scale means 104, or 10x10x10x10 = 10,000
Trichlor is 10,000 times more acidic than pure water.
Don’t worry about the math, it’s just to explain the pH scale itself. From a water chemistry perspective, the ideal pH for a swimming pool or spa is between 7.4-7.6. If your pH is higher (more alkaline), you can lower it by injecting carbon dioxide (CO2) or adding some muriatic acid. If your pH is lower (more acidic), you can raise it by adding something alkaline, like soda ash or sodium bicarbonate (baking soda).
The role of pH in water chemistry
Managing pH is a critical component of maintaining healthy water chemistry. It is so important because pH is a driving factor in the Langelier Saturation Index (LSI), and also because pH determines how effective chlorine will be. The lower the pH, the stronger chlorine will be. That being said, it is also important to understand that the type of chlorine you use affects both pH and total alkalinity. That’s because different types of chlorine have very different pH levels. For example, Trichlor (mentioned above) has a low pH. But Calcium Hypochlorite (Cal Hypo) has a high pH of almost 12.
As an aside, never mix different types of chlorine. They can explode. Literally.
Low pH can cause damage to pool liners and etching of plaster; corrosion of metal components in and around the pool; skin and eye damage, as well as general patron discomfort; and a reduction of total alkalinity. On the other hand, high pH water can cause scale formation; metal stains; cloudy water; poor efficiency of chlorine, and also can cause skin and eye irritation. The textbooks say to stay within the 7.4-7.6 range to avoid those problems. But we at Orenda know that scale formation and plaster etching are a function of LSI violations, not just pH.
What is Total Alkalinity?

Unlike pH—which is basically an equilibrium scale to measure against—total alkalinity is a measurement of the concentration of all alkaline substances dissolved in the water. These substances are primarily carbonates, bicarbonates and hydroxides, along with a few others. These alkaline substances buffer pH in the water by neutralizing acids. In other words, total alkalinity is a measurement of the water’s ability to resist change in pH.
Total alkalinity is measured by its concentration in parts-per-million (ppm), and the ideal range is from 80-120ppm, depending on the type of chlorine you use. For example, Trichlor has a low pH of about 3, which means you will want your total alkalinity closer to 120ppm, given how acidic Trichlor is. Liquid chlorine (bleach), however, has a high pH of 13, so you can have lower alkalinity, like 80-100ppm. Note: one of the byproducts of using liquid bleach (sodium hypochlorite) is sodium hydroxide, which contributes to total alkalinity and raises pH.

Did you notice that total alkalinity is not measured on the pH scale?
This is an important distinction to make, because this is usually how pH and alkalinity get confused. Total alkalinity is measured by the amount, or concentration (ppm) in the water, not by how alkaline (pH) the water is. ‘Alkalinity up’ products are prevalent in the pool industry. If you are in the market for an alkalinity increaser, the two most common are sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), more commonly known as soda ash. ‘Alkalinity down’ products will be an acid like muriatic acid or sodium bisulfate
The role of total alkalinity in water chemistry
If you’re a pool operator, you probably already know that pH can fluctuate up and down. And when it does, the pool is constantly fighting against you. Having the right level of total alkalinity is a good thing, because it helps to keep the pH stabilized. A simple way to think about this is alkalinity neutralizes acids.
Technically, alkalinity buffers pH by either providing or absorbing a Hydrogen ion (H+) as needed. So when acid is added, carbonate ions can absorb Hydrogen to create bicarbonate ions. This is an equilibrium, just like pH, so it can go the other way too. The equilibrium looks like this:

HCO3- + H+ ↔ H2CO3
You could have a ton of 8.3pH Sodium Bicarb floating around in the water, and have the same pH as if you added a much smaller amount of 13.0pH soda ash. But the total alkalinity would be higher for the Sodium Bicarb, because there’s simply more of it in the water.
How to increase total alkalinity
If you want to increase total alkalinity in a swimming pool, you need to know the gallonage of the
pool, and your pH. It helps to have an accurate dosing calculator. Raising alkalinity is as simple as adding carbonates, bicarbonates or hydroxides to the water. As mentioned before, two of the most common pool products are sodium carbonate (soda ash) and sodium bicarbonate (sodium bicarb).
How to lower total alkalinity
You can lower alkalinity using acid. Some experts recommend a “acid column pour” to lower alkalinity, but we do not. In our experience–and indeed, scientific experiments back this up–column pouring is no more beneficial than dilution. We recommend diluting the acid in a bucket of water, and evenly pouring it around the pool. Besides, column pouring can severely lower the pH in a concentrated location (at the bottom of your pool!), which can throw the LSI off, and in turn, etch the surface.
Lowering pH without affecting total alkalinity can be accomplished using carbon dioxide. But that’s a topic for another time.

Final thoughts
Maintain your pool within LSI balance, first and foremost. Then, try to keep your total alkalinity within the range of 80-120ppm for healthy pool chemistry. Use an alkalinity increaser like sodium bicarbonate to raise total alkalinity, or an acid to lower it. When using high-pH chlorines like liquid bleach or Cal Hypo, stay lower in the range, like 80-100ppm. For low pH chlorines like Trichlor, 110-120ppm is where you want to be. Consult your test kit or the dosing calculator on the Orenda App for specific numbers.
People confuse pH vs. alkalinity and we can understand why. Just remember that pH is an equilibrium that functions like a scale measuring how acidic or how basic a substance is. Total alkalinity measures the amount or concentration (in parts per million) of dissolved bicarbonate, carbonate and hydroxide ions. We hope this helps!
summarize water chemistry for betta
pH is the acidity or alkalinity level of water, while Total Alkalinity (TA) is the ability of water to resist changes in pH to maintain a stable and safe water balance for Betta fish.
Looking for Rare betta fish?
If this article water chemistry was useful to you You can leaving a 5-star reviews for It’s an encouragement. For us make encourage us in our research. Research information about betta fish for to present useful information further

Also we have group talk about betta fish for sale and share any new tip take care information on Web3 socialFi group

Right now we have betta fish doctor help every bettas lover by top breeder in Thailand to cure or share more tip on Animalverse social
If your bettas fish sick or need tip to treat help or join event prize with AVC Token
Let’s join the group many top breeder will help to answers in betta fish community
More tip :
How to breed betta fish for the desired color
All of Betta Fish A Guide on Patterns, Color in the world
What the difference between male and female betta fish
What are the bubbles top betta fish tank
The most expensive betta fish in the world.






